U.S. consumer prices rose 0.3% in June, marking the largest monthly increase in five months and pushing the annual inflation rate to 2.7% from 2.4% in May.
This acceleration exceeded expectations of a 2.6% annual headline inflation print and highlighted emerging pressures from trade policies, though core inflation still fell short of estimates on a monthly basis.
Excluding food and energy costs, price pressures ticked 0.2% higher month-on-month versus the 0.3% forecast but the annual core reading still rose to 2.9%.
Key Takeaways
- Headline CPI: +0.3% monthly (vs. 0.3% expected), +2.7% annually (vs. 2.4% prior)
- Core CPI: +0.2% monthly (vs. 0.3% expected), +2.9% annually (vs. 2.8% prior)
- Shelter costs: Rose 0.2% monthly, continuing as primary driver of inflation
- Energy sector: Gained 0.9% with gasoline prices up 1.0% for the month
- Food inflation: Increased 0.3% monthly, with food away from home up 0.4%
- Early tariff signals: Price pressures evident in household furnishings (+12.4% annualized), recreation goods (+9.7%), and clothing (+5.3%)
Early evidence of tariff-related price increases appeared in several categories. Fruits and vegetables surged 11.5% on a seasonally adjusted annualized basis, while home furnishings jumped 12.4% with broad-based increases across furniture and appliances.
Link to official U.S. Consumer Price Index (June 2025)
However, offsetting factors provided some relief. The crucial shelter component, which carries a 40% weighting in core CPI, showed moderation with a 0.2% monthly increase. New vehicle prices declined 0.3% and used cars fell 0.7%, defying expectations of tariff-driven increases in the automotive sector.
The softening in core goods prices, particularly the 0.04% monthly decline excluding vehicles, suggests tariff impacts may be more delayed than initially anticipated. This aligns with historical patterns where tariff effects typically emerge approximately three months after implementation.
Market Reaction:
U.S. Dollar vs. Major Currencies: 5-min
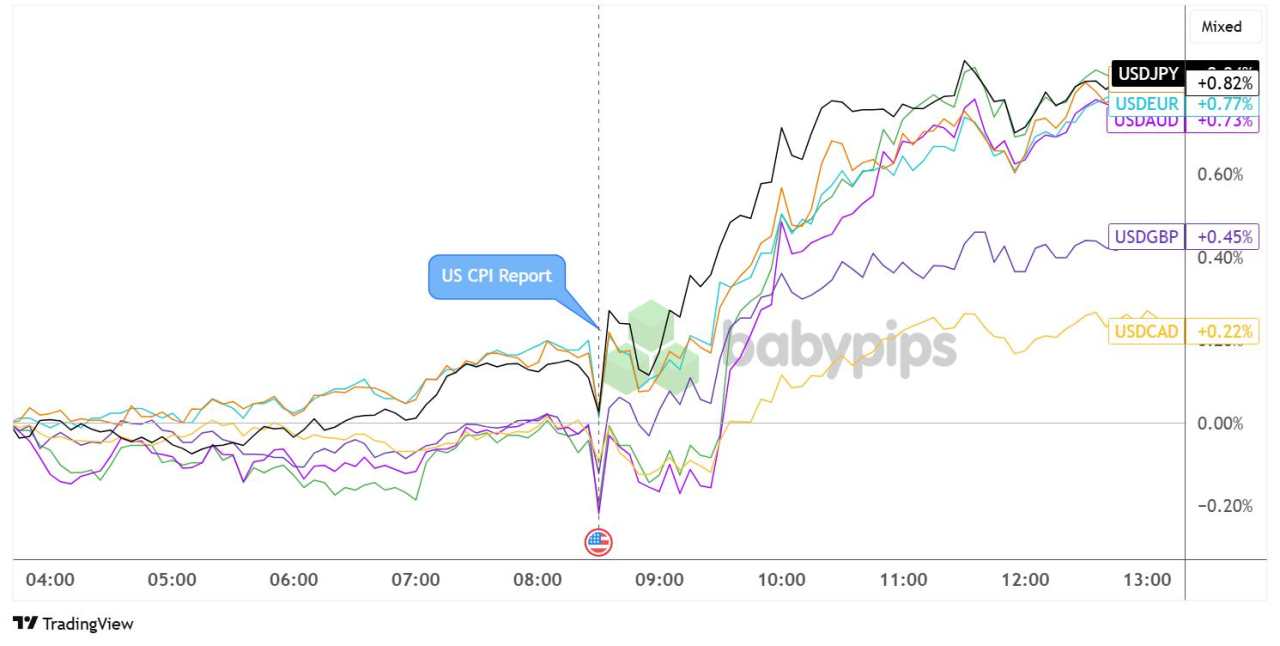
Overlay of USD vs. Major Currencies Chart by TradingView
The dollar strengthened broadly following the CPI release, with the USD gaining against major currencies as traders scaled back Federal Reserve rate cut expectations.
According to the CME FedWatch Tool, the probability of a July rate cut dropped to just 2.6% from around 6% earlier in the week. September rate cut odds also decreased to approximately 54% from nearly 60%, reflecting market participants’ reassessment of the Fed’s likely policy path.
Price action for the rest of the U.S. session showed the dollar’s resilience, with notable gains against the Japanese yen (+0.82%), euro (+0.77%), and Australian dollar (+0.73%) hours after the CPI release.


加载失败()